Tutorial Intro
Let's discover EU DCC in less than 5 minutes
Getting Started
Get started by by creating, signing, and verifying a new certificate..
What you'll need
- Node.js version 14 or above:
- When installing Node.js, you are recommended to check all checkboxes related to dependencies.
- The JavaScript and shell scripts in the ehn-sign-verify-javascript-trivial repository.
Checkout the repository
Check out the ehn-sign-verify-javascript-trivial repository.
git clone https://github.com/ehn-dcc-development/ehn-sign-verify-javascript-trivial.git eu-dcc-start
cd eu-dcc-start
You can type this command into Command Prompt, Powershell, Terminal, or any other integrated terminal of your code editor.
The cd command changes the directory you're working with.
In order to work with files you checked out, you'll need to navigate the terminal there.
You could also use degit instead of git clone to clone that repository.
Install all the dependencies
npm install
Generate CSCA and DSC certificates
CSCA and DSC certificates will be used for signing and verifying the EU-DCC certificate we will create.
All the shell commands for creating the certificates are in the gen-csca.sh scripts, so run the following command:
./gen-csca-dsc.sh
The script will generate the following files:
- Certificate Authority:
csca.pem - Private key:
dsc-worker.key - Private key in
p8format:dsc-worker.p8 - Public key:
dsc-worker.pem
Create and Verify Certificate
Create and Sign
First, create the payload you will attach to the certificate.
echo '{ "fname": "John", "lname": "Smith" }' > payload.json
Now you are ready to attach this payload to the certificate and sign it.
cat payload.json | npm --silent run sign > my-dcc.cert
This command will create the my.cert file which a fully signed certificate with the above payload attached.
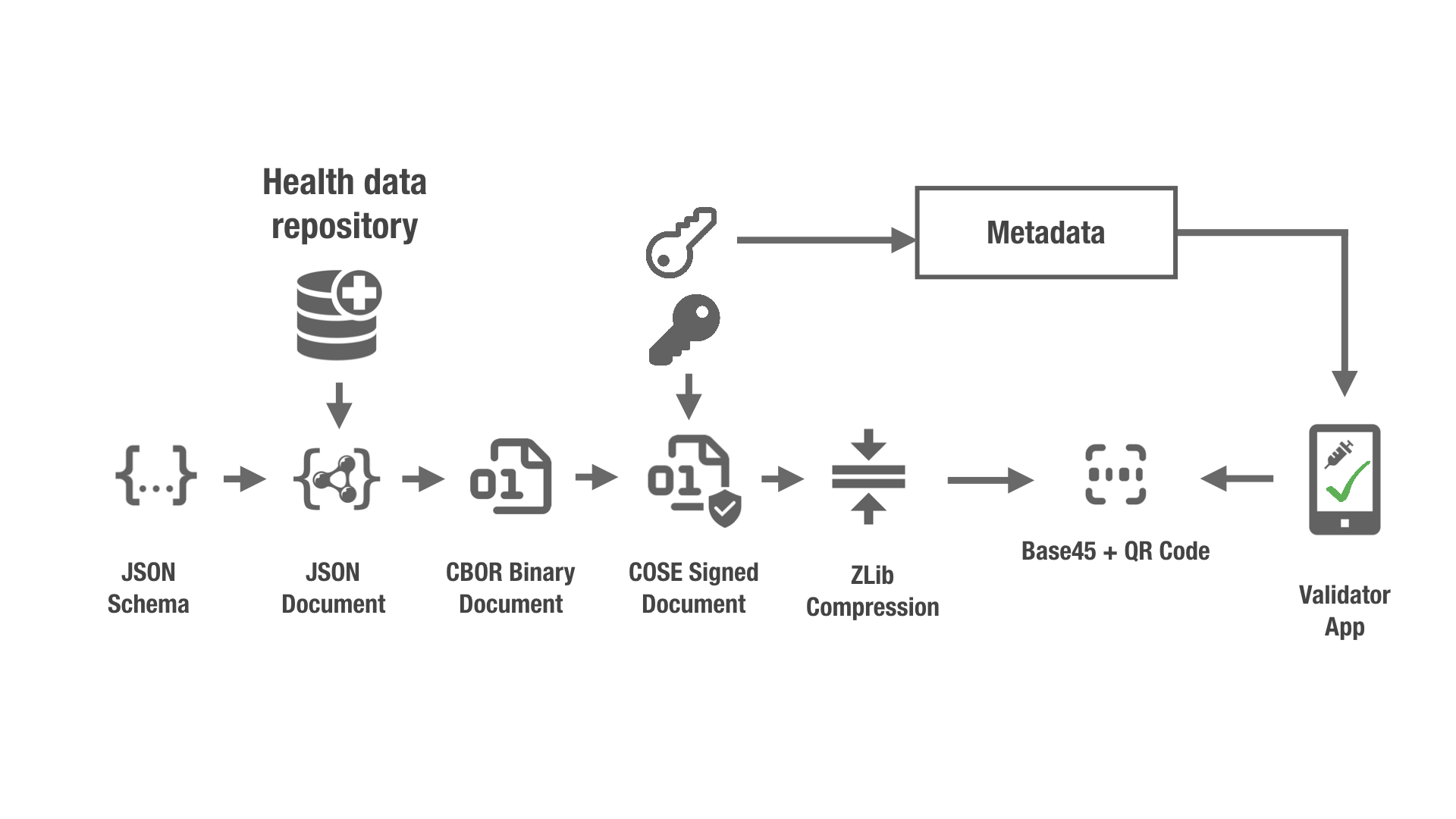
The process for producing it follows the steps:
- Compact the JSON into CBOR.
- Sign and package the CBOR as a COSE message.
- ZLIB compress the message.
- Base45 encode and generate the final string.
See the string representation of the certificate by entering the command:
cat my-dcc.cert
HC1:6BF580B30FFWTWGSLKC 4+59TYJZ10M8J6AO76B%NKW.CBEC CKI949D: C..DF$DJ CJ$DAWE27BM+3*-L28VKNS6SL3UPDJIYP9YO0.J0:*Q DPNOQJFLE0UKDK%/E+U77WSIVG:EW+ M88KWMQ::F3J3DOIY3T40OK%74V25-139J-L6
Unpack and Verify
For verifying the EU-DCC Certificate you just created you need to follow the reverse process:
- Base45 decode the string in the
my-dcc.certfile. - ZLIB decompress.
- Verify the COSE signature unpack it into a CBOR document.
- Unpack the CBOR document into JSON.
Run the command:
cat my-dcc.cert | npm --silent run verify
The verifying process uses the public key in the dsc-worker.pem file verifying the COSE signature.
If the signature is valid it proceeds, unpacks the document, and displays the JSON payload.
Output:
{
"fname": "John",
"lname": "Smith"
}
Live
Check this tutorial live in replit